Research
Blockchain Gaming Part 1: Ecosystem Research
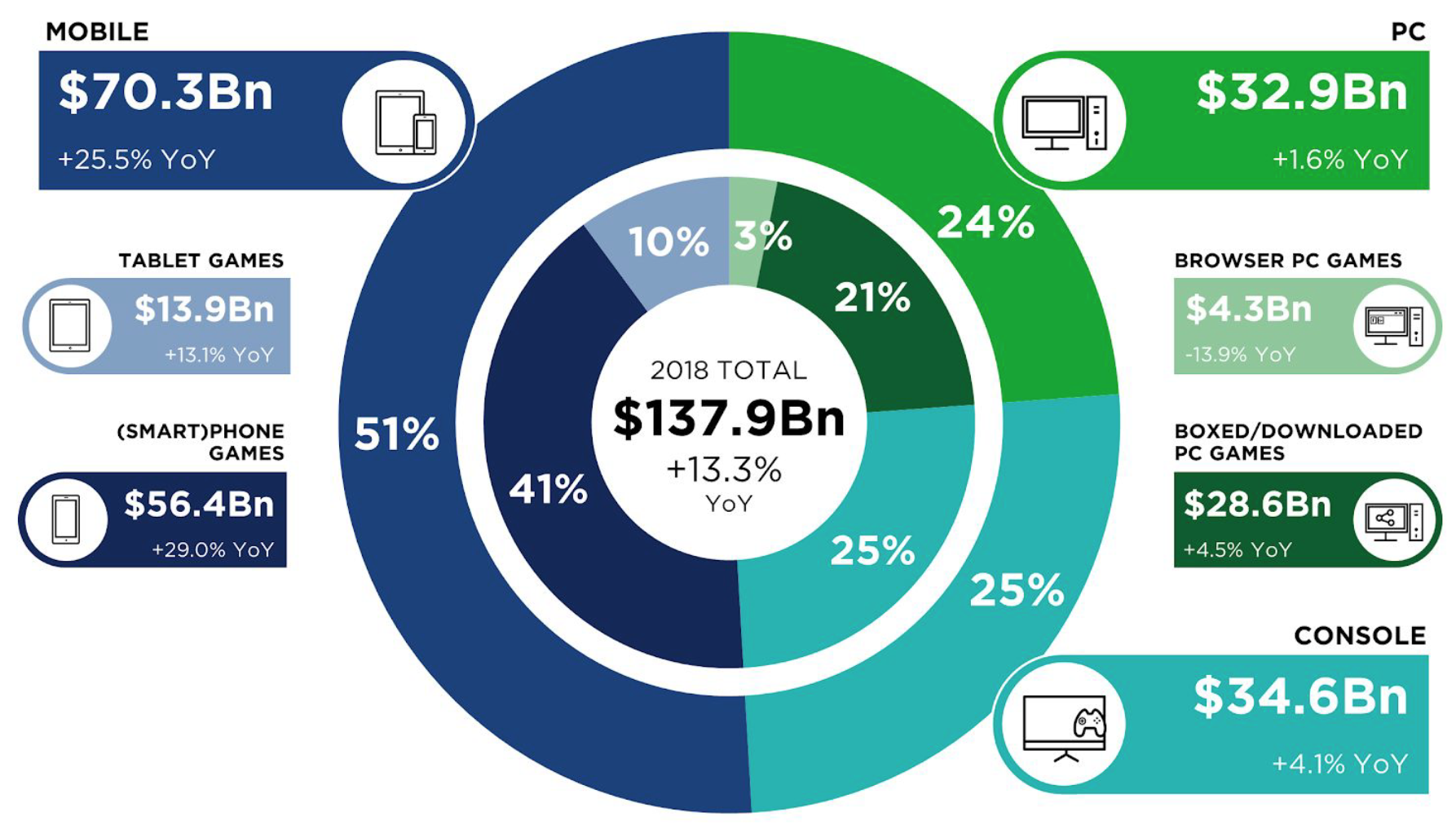
The global games industry is $138Bn by revenue and has grown $67Bn in the last five years, driven by the explosion of mobile gaming. Hence, today blockchain-based games are a small but growing piece of the global gaming industry.
Video Game Addressable Market
- The global games industry is $138Bn by revenue
- The industry has grown $67Bn in the last five years, driven by the explosion of mobile gaming
- ~$5Bn in total transactions1 were processed on the Ethereum, EOS and TRON blockchains in 2018
- Hence, today blockchain-based games are a small but growing piece of the global gaming industry
Blockchain-Based Gaming Rationale
Smart Contracts for Fair Gameplay
- Today most gaming software (the graphics, the gameplay and the currency) is all proprietary
- Everything is controlled by operators, which puts players at the whim of changes by game developers and publishers
- With blockchain-based games, developers can program open-source smart contracts to determine payout functions, ensuring fairness in gameplay
Fungible Tokens as Currency
- Blockchain-based games can use cryptocurrencies (fungible tokens) as a cross-platform payment mechanism
- Many existing games have their own in-game currency. Unless they are cryptocurrencies, their value is not transferable to other games
- Cryptocurrencies as a payment mechanism are the only way that smart contracts can process and issue digital assets
Non-Fungible Tokens for Digital Assets
- A non-fungible token (NFT) can be used to uniquely identify an asset in a game (i.e. a rare sword won from a particular boss or a gamer’s reputation)
- If many different games use the same NFT standard for in-game assets, creations will have resale value outside of their game and be traded in marketplaces
Blockchain and Video Gaming Have an Interconnected History
It’s arguable that digital assets in video games led to the emergence of cryptocurrency

World of Warcraft Gold
- World of Warcraft has an in-game currency (which was uncommon at the time) called World of Warcraft Gold
- The process was simple: purchase the gold with fiat currency and then use it to buy things in the game. Certain items that could be stolen from some of the toughest bosses became extremely valuable
- Given the popularity of WoW, this marked the emergence of digital assets with real value at scale
Digital Asset Farmers
- Gamers who recognized the emergence of digital assets with real value began “farming” these rare items and selling them for a premium at a later date
- This is seen by many as the predecessor to crypto mining
- Brock Pierce, Jonathan Yantis and Steve Bannon (then of Goldman Sachs) joined forces at Internet Gaming Entertainment (IGE), entered around this concept
WoW Gold vs. Crypto
- WoW gamers became comfortable with these online transactions, digital markets, & converting their digital money back into fiat
- The difference between WoW Gold and Bitcoin is that the Gold is centrally owned and possessed by developers, while Bitcoin is owned/possessed by players in their digital wallets
- The central ownership of Gold allowed developers to halt transactions and ban users from “misbehaving”
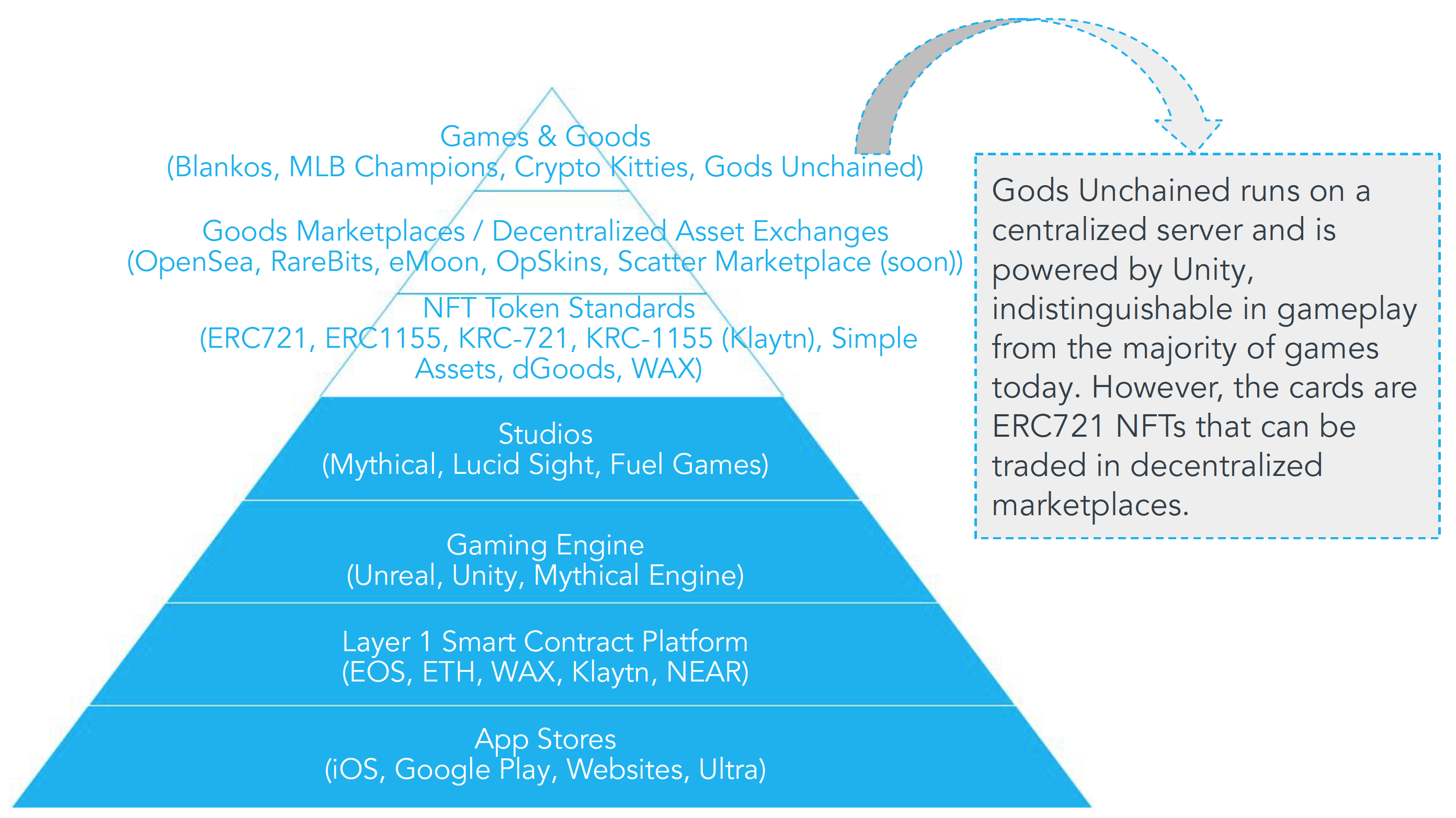
The Blockchain Gaming Stack
Two Types of Blockchain Games Today
Roleplay or Collectibles
- Most blockchain-based games in the market today are either roleplay games or digital collectible games
- Roleplaying games are essentially dynamic digital collectible games, where items in the storylines develop tradeable value
Gambling
- Blockchain gambling dApps have become the easiest onramp to gambling for users, as most blockchain gambling sites are not licensed
- Cryptocurrency, decentralization, and smart contract integration helps to bring transparency to payout models in online gambling and solves many of the industry’s fundamental pitfalls
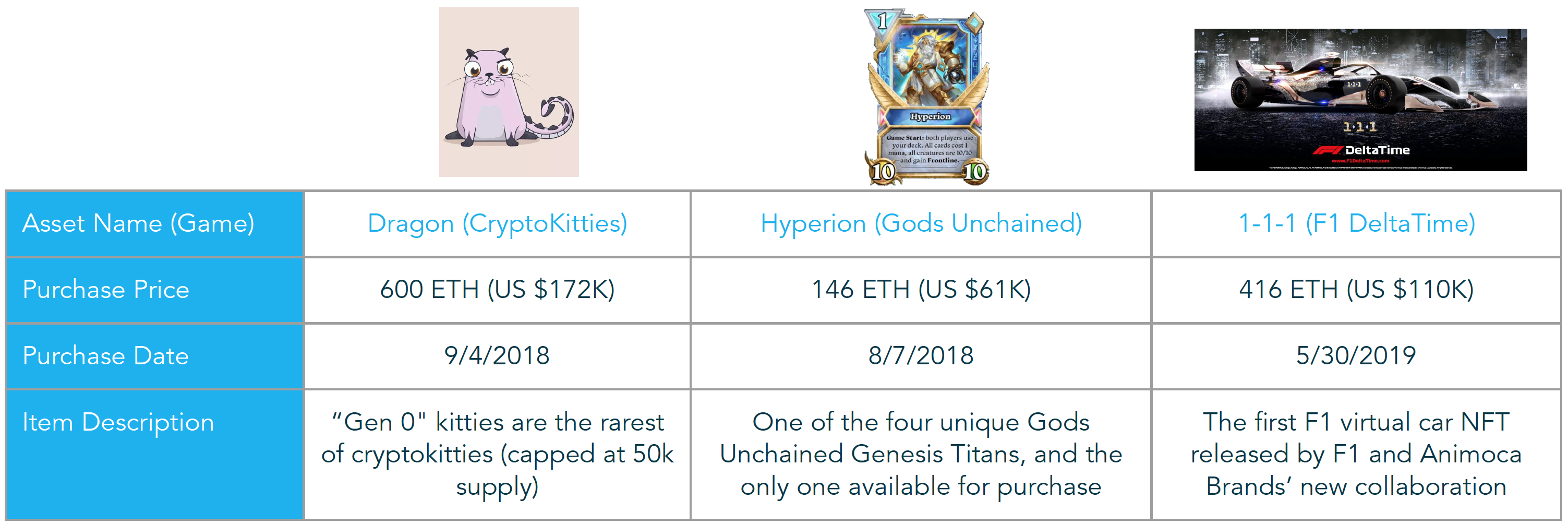
Digital Collectibles Have Proven, Real-World Value
How much would a fan pay to own an original character of Fornite legend Ninja after he retires?
- If blockchain can prove players truly own certain assets, the gaming community is passionate enough that they would pay substantial amounts for certain items
- The limited number of games that have integrated blockchain have proven this to be true
How to Access Blockchain-Based Video Games
For now, all blockchain-based video games are PC and mobile based. Players are connected through hot wallets

Blockchain Game Analytics
DappRadar is the main analytics platform and ranking engine for blockchain dApps that tracks number of users, number of transactions and transaction volume per game
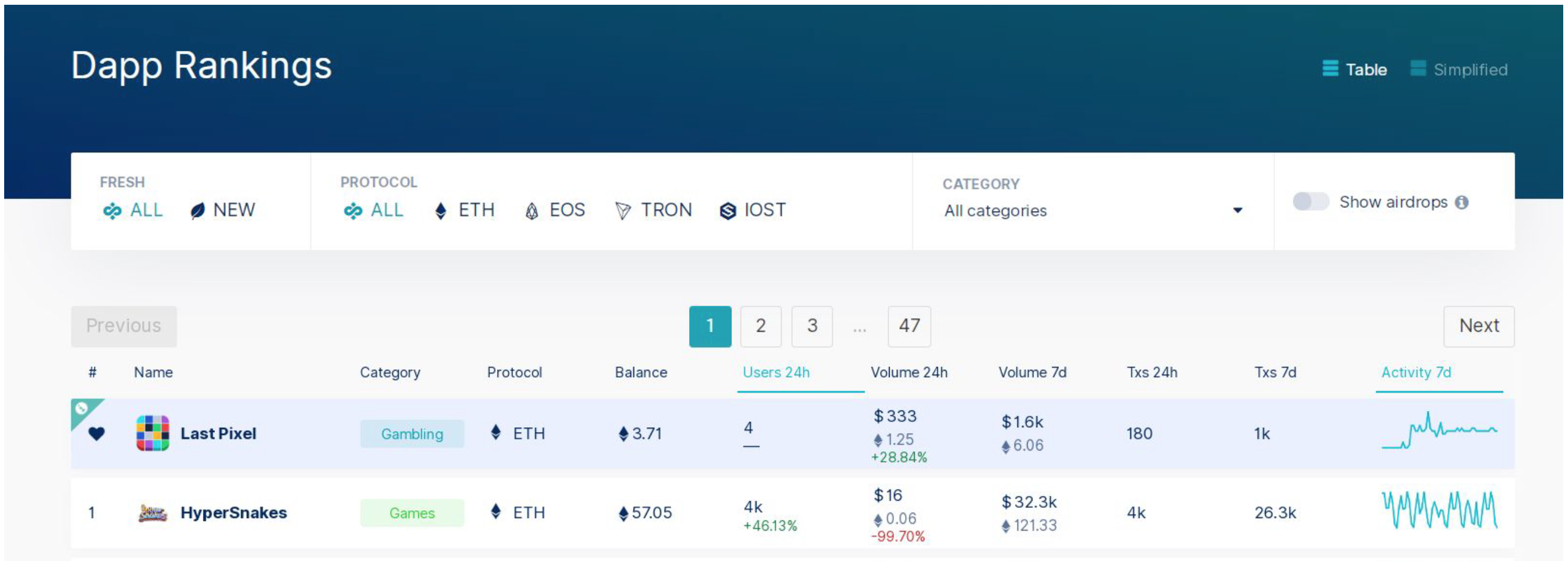
dApps with the highest usage are games, despite the hype around decentralizing all types of applications
Top 5 Blockchain Games on DappRadar Today
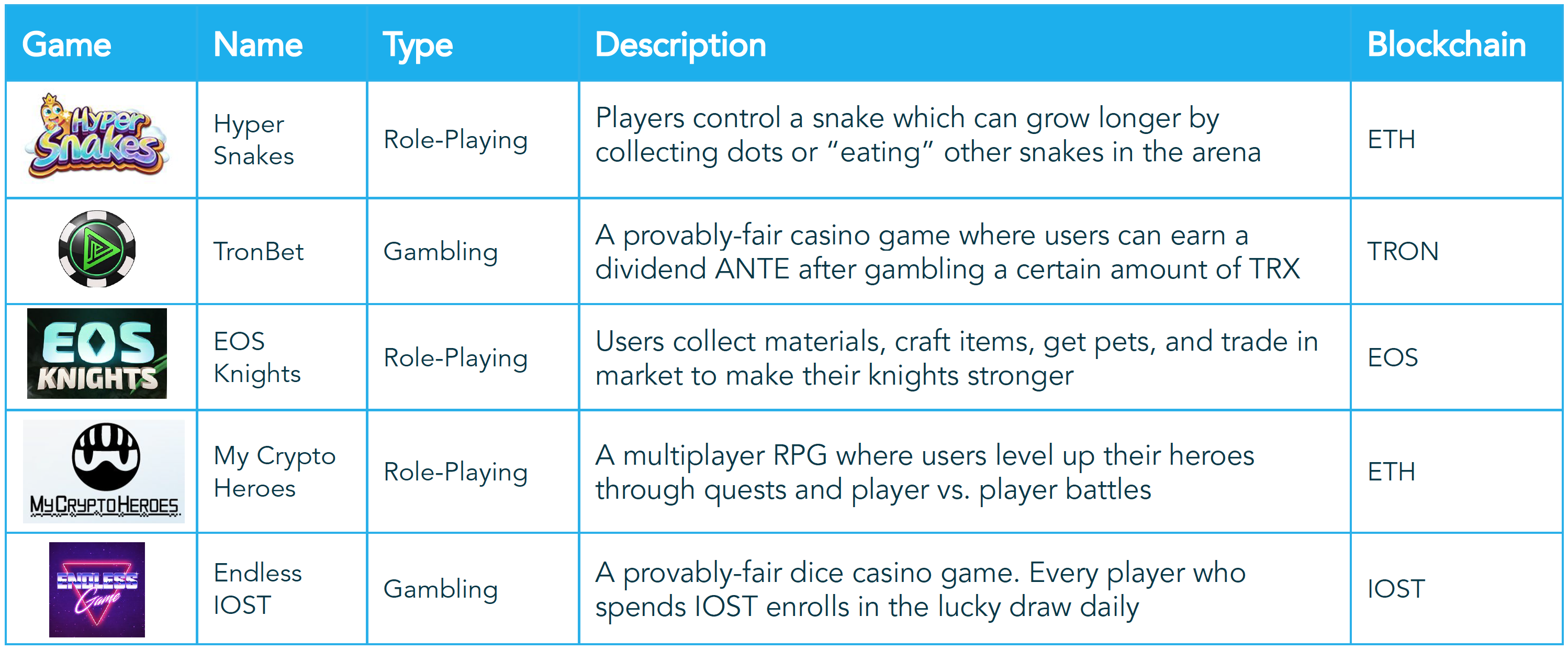
Rankings as of 6/18/19, ranked by number of users. Unclear today how much usage is real vs. artificially created by bots.
Leading investors for blockchain gaming

Challenges for Blockchain-Based Gaming
1. Onboarding:
- Getting gamers to join the blockchain is a pain
- Can developers make the blockchain invisible?
2. Item-first gaming is expensive:
- You need to buy items to play
- Can we make games F2P? i.e. Cryptage Origins
3. Transactions are expensive:
- Writing data on the blockchain costs time & gas
- Can we make Tx fast & free? I.e. Loom, Efinity, Tenfold (layer 2 solution examples)
4. Immature & inaccurate data analytics:
- How much volume is real vs. generated by bots?
This is part one of a three part series. Click here for part 2.
—
Wave Financial, LLC is a Registered Investment Advisor (CRD#292343). This article is for general informational purposes only. Nothing herein is an offer to buy or sell, or the solicitation of any offer to buy, any security or interest in any investment, nor is it intended to be used for marketing purposes to any existing or prospective investor in any jurisdiction, and is subject to correction, completion and amendment without notice.






You must be logged in to post a comment Login